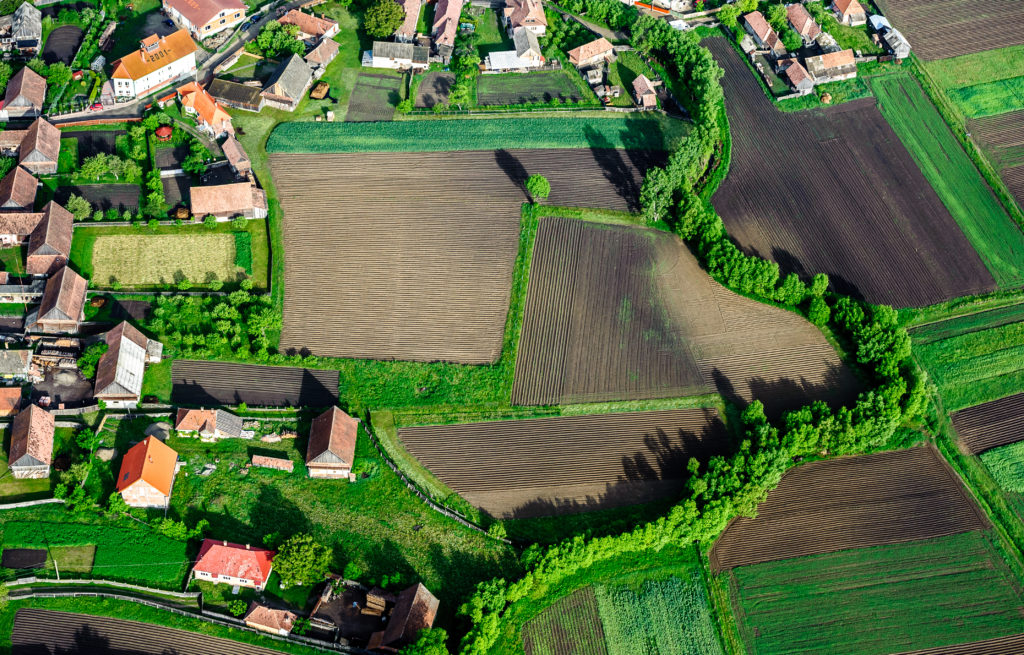
Land subdivision plays a vital role in modern land development and real estate markets. It is the process of dividing a larger parcel of land into smaller, legally defined lots that can be sold, leased, or developed individually.
Understanding the benefits of land subdivision is important before deciding whether to pursue this type of project. While subdivision requires careful planning and regulatory approval, it can offer long-term financial, community, and environmental advantages when done correctly.
This article explores the key benefits of land subdivision, highlighting how it can increase land value and support sustainable growth.
Increased Land Value and Financial Opportunities
One of the most significant benefits of land subdivision is its ability to increase overall property value. A large parcel of land may have limited appeal to buyers due to its size, cost, or development complexity. By subdividing the land into smaller lots, the owner can make the property more accessible to a wider range of buyers.
Selling multiple lots individually often results in higher combined value than selling the land as a single parcel. This approach allows landowners to maximize returns while spreading sales over time, providing more flexible cash flow opportunities.
Subdivision also creates opportunities for development-based cash flow. Landowners may choose to sell some lots while developing others, lease parcels, or partner with builders. This flexibility makes land subdivision an attractive strategy for long-term investment and wealth creation.
Improved Marketability and Property Use
Subdividing land improves marketability by aligning lot sizes with buyer demand. Many homebuyers, businesses, and developers prefer smaller, clearly defined parcels that are easier to finance, develop, and maintain. Subdivision allows landowners to tailor lot configurations to current market needs.
Smaller lots are often easier to appraise and finance, making them more attractive to lenders and buyers. Clear legal boundaries and recorded subdivision plats reduce uncertainty, helping transactions move more smoothly.
In addition, subdivision enables more efficient land use. A single large parcel may not be practical for multiple purposes, but subdivided lots can support residential, commercial, or mixed-use development. This adaptability increases the property’s appeal across different market segments.
Support for Planned Growth and Development
Land subdivision supports orderly and planned growth by ensuring development follows established zoning and land-use regulations. Local governments use subdivision standards to guide how land is divided, helping prevent overcrowding, access issues, and incompatible land uses.
Through the subdivision process, developers must consider road access, lot layout, building setbacks, and utility connections. This planning helps create well-organized developments that integrate smoothly with surrounding areas.
By encouraging structured growth, subdivision reduces land-use conflicts and promotes long-term community stability. Properly planned subdivisions align with comprehensive plans and contribute to predictable, sustainable development patterns.
Infrastructure and Community Development Benefits
Subdivision often leads to improvements in infrastructure and public services. As part of the approval process, developers may be required to install or upgrade roads, sidewalks, drainage systems, and utilities. These improvements benefit both new developments and surrounding neighborhoods.
Well-designed subdivisions enhance access and connectivity, making areas safer and more functional for residents and businesses. Improved infrastructure can also increase nearby property values and attract additional investment.
In many cases, subdivision projects contribute to community amenities such as parks, open spaces, or pedestrian pathways. These features enhance quality of life and help create more livable, attractive neighborhoods.
Environmental and Land Management Advantages
When carefully planned, land subdivision can support better environmental management. Developers can designate conservation areas, open space, or buffer zones within a subdivision, preserving natural features while still allowing development.
Subdivision regulations often require proper stormwater management, erosion control, and drainage planning. These measures help protect waterways, reduce flooding risks, and minimize environmental impacts.
Additionally, subdivision allows landowners to plan development in phases, reducing disruption to natural landscapes. This structured approach supports sustainable land use and responsible growth that balances economic and environmental considerations.
Conclusion
Land subdivision offers numerous benefits for landowners, developers, and communities alike. By increasing property value, improving marketability, supporting planned growth, and enhancing infrastructure, subdivision plays a key role in modern land development.
While the process requires careful planning and regulatory compliance, the long-term advantages often outweigh the initial challenges. With professional guidance and a clear strategy, subdivision can unlock new opportunities and create lasting value.